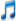Ipak akatsiya
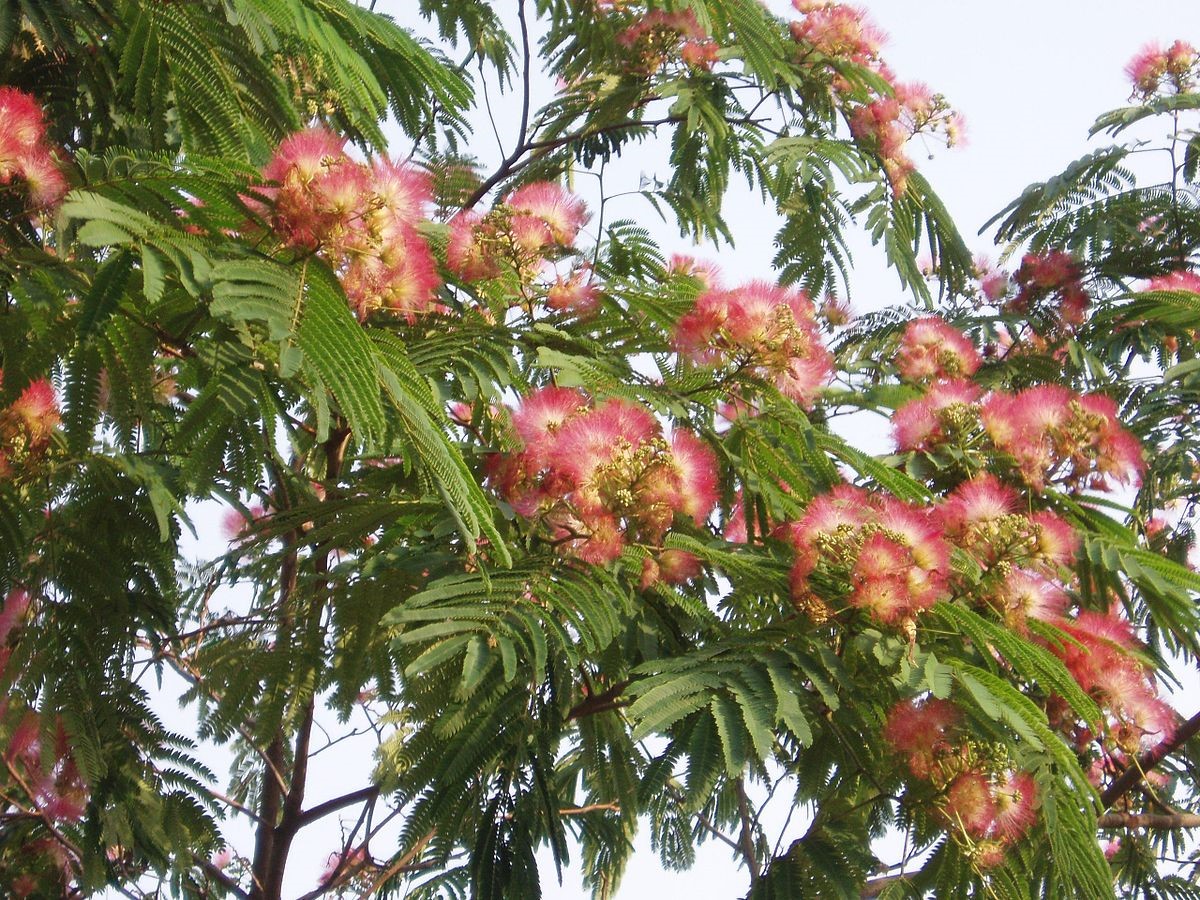

 Albizia Lankaran (Latin Albizia julibrissin) is a species of trees of the genus Albizia of the Legume family (Fabaceae). It is used as an ornamental plant in gardens and parks. The height of the tree is 6-9 (up to 16) meters. It has a sprawling, or mostly umbrella-shaped, openwork crown 6-7 meters wide. The leaves are unpaired, double-feathered, openwork, consist of 9-15 lobes, each of which contains 15-30 pairs of leaflets sitting on a secondary petiole; the leaflets are dark green above, whitish below. The length of the leaf reaches 20 centimeters. In hot weather and at night, the leaves are folded along the middle vein, and the entire complex leaf droops. In winter, albizia sheds its leaves. Blooms in May—August. The flowers are yellowish-white, marginal infertile — staminate, central bisexual, have 5-ray symmetry, collected in corymbose panicles. Stamens are long, pink or white in color. Albizia fruits are flat multi-seeded beans, green in youth, straw-yellow or brownish in adult states, 10-20 cm long. Seeds are elongated oval, flat, dull, brown or brown, 6-7 mm long. The tree grows fast, lives 50-100 years.
Albizia Lankaran (Latin Albizia julibrissin) is a species of trees of the genus Albizia of the Legume family (Fabaceae). It is used as an ornamental plant in gardens and parks. The height of the tree is 6-9 (up to 16) meters. It has a sprawling, or mostly umbrella-shaped, openwork crown 6-7 meters wide. The leaves are unpaired, double-feathered, openwork, consist of 9-15 lobes, each of which contains 15-30 pairs of leaflets sitting on a secondary petiole; the leaflets are dark green above, whitish below. The length of the leaf reaches 20 centimeters. In hot weather and at night, the leaves are folded along the middle vein, and the entire complex leaf droops. In winter, albizia sheds its leaves. Blooms in May—August. The flowers are yellowish-white, marginal infertile — staminate, central bisexual, have 5-ray symmetry, collected in corymbose panicles. Stamens are long, pink or white in color. Albizia fruits are flat multi-seeded beans, green in youth, straw-yellow or brownish in adult states, 10-20 cm long. Seeds are elongated oval, flat, dull, brown or brown, 6-7 mm long. The tree grows fast, lives 50-100 years.
The natural range of the plant covers several regions of Asia (from Iran to Taiwan):
Front Asia: Iran, Turkey, south-east of Azerbaijan.
East Asia: China, North Korea, South Korea, Japan (Hokkaido, Honshu, Kyushu, etc.), Taiwan.
Indian Subcontinent: Bhutan, India, Nepal, Pakistan.
Southeast Asia: Myanmar.
To the Tashkent Botanical Garden Albizzia julibrissin Durazz. The seeds of the species are A.A. Mavjudov in 1971 for the purpose of introduction and planted in nurseries. The sprouts planted from the seeds were unub in March 1972, and the young sprouts were transplanted into the European-Crimean-Caucasian exposition collection on April 20, 1972. Currently, 5 adult trees of this type of tree are growing in this exposition.