Area
Distributed in Eurasia, Brazil and the Andes.
Botanical description of the plant
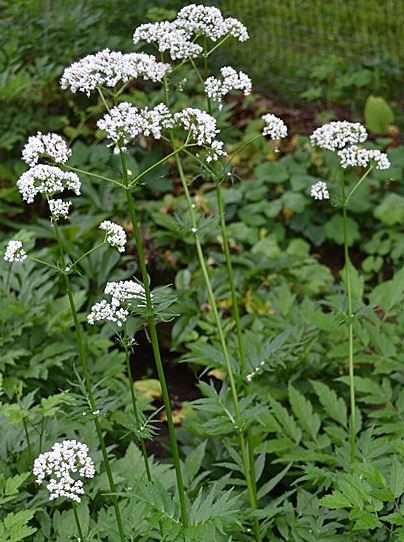
Medicinal valerian - Valeriana officinalis L, a perennial herbaceous plant belonging to the family Valerianaceae (Valerianaceae), with a short rhizome and many small roots, located vertically underground. In the first year from the rhizome take root tubers, from the second year the stem grows. Stems erect, growing up to 1.5-2.0 meters. Cylindrical, fine-edged unbranched (sometimes branched at the top), hollow inside, hairless at the top and hairy at the bottom. The leaves are simple, odd-haired, 4-11 pairs of segments. If the rhizome leaves are long-banded, the band of leaves on the stem will shorten as it reaches the top of the stem. The leaves are located opposite the stem. The flowers are small, fragrant, clustered in a large shield at the end of the stem. The cup leaves are not clearly visible as they are turned inwards towards the flower. The inflorescence is five-lobed, the tip is turned inwards, white or pink, the paternal 3 maternal nodes are 3-lobed, located below. The fruit is an elongated ovoid, light brown pistachio. Seeds of valerian plant weigh 0.4–0.6 grams per 1000 grains. It blooms from late May to August-September.

Medicinal properties
In medicine, the dried roots and surface of the plant are used. The root contains 0.5-1.0 essential oils, 0.5-2.0% valeotriates, alkaloids, isovalerian, vinegar, organic acids such as vinegar, saponins, preservatives and other substances. Therefore, medicinal preparations of the plant (root powder with roots, tablets, tinctures, decoctions, tinctures, liquids, tablets of thick extract) calm the nervous system, strengthen the heart muscle and nerve fibers, dilate blood vessels, normalize blood circulation, digestion. accelerates the process of digestion in the organs and helps them to be absorbed. Medicinal valerian drugs are also of great importance in insomnia. In addition to the above, the root and rhizome of the plant are included in herbal teas used as a sedative in diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, liver, gallbladder, kidney and respiratory tract. There is a lot of information that it is the main medicinal plant in the treatment of hypertension and neurological diseases. The bioorganic active substances in it improve the activity of the thyroid gland in the body.
Growing technology
In autumn, the land is plowed, leveled, chiseled and cleared of weeds, 60 cm wide is sown, 7-8 kg of seeds are sown per hectare, the depth of planted seeds should not exceed 1-1.5 cm. Valerian seeds are resistant to frost and germinate when the soil temperature is 50 C. However, the optimum level of seed germination is 15-200 C. In periods when the weather is good, the seeds germinate 15-20 days after planting. In the second and subsequent years of vegetation, valerian grass sprouts as soon as the snow falls from the ground. Valerian care begins with loosening and mowing the lawn. Sprouted seedlings are fed with local and mineral fertilizers. It is recommended to apply 30-40 kg of nitrogen and phosphorus mineral fertilizers per hectare. During the processing of valerian, overgrown flower stalks are removed so that its underground rhizome and root mass are large. Valerian can also be propagated by seedlings in addition to seeds. For this purpose, a special nursery is established, seedlings are grown and the seedlings are transplanted to open ground. The spacing of each seedling should be 10–15 cm and watered immediately.