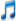Acer palmatum

 The yellow-leaved maple or Japanese maple (Acer palmatum Thunb. (Lab.)) is a perennial tree of the turi, order Zarang, family Sapindaceae. Distribution: Japan and Korea. The branches of the tree are reddish-gray, the bark is gray, smooth, 8-15 CM in diameter, the edges are toothed, Seven, Nine, Eleven-piece 3-5 cm long, often in a slightly pubescent autumn the leaves are orange-red with yellow spots, the flowers are bright, purple-red, the fruit is rather elongated, formed in front of the leaves in April. The tree is of a low growth type and grows to a height of about 6 meters. The leaves are initially green, red-purple to black-purple, turning red in autumn. The flowers are small, purple, the fruit is red. Propagated by grafting or soft twigs. Prefers to grow in neutral alkaline soil, rich in organic matter, as well as well-drained, slightly acidic. Very favorable conditions were considered for its growth both in the sun and in partial shade. Treated as an ornamental plant, the color of its leaves is used for planting singly or in groups in landscape design, as it has an irreplaceable appearance on other trees. Introduced to the Botanical Garden. The seeds of this species were brought from Antwerp and sown in the Botanical Garden by academician A.A. Mavzhudov in 1971. In 1972, in the spring, the nursery was sown and the introduction of these species was studied, and in 1973 they were planted in the East Asian exposition. Currently, 1 adult year of the tree of this species grows in this exposition.
The yellow-leaved maple or Japanese maple (Acer palmatum Thunb. (Lab.)) is a perennial tree of the turi, order Zarang, family Sapindaceae. Distribution: Japan and Korea. The branches of the tree are reddish-gray, the bark is gray, smooth, 8-15 CM in diameter, the edges are toothed, Seven, Nine, Eleven-piece 3-5 cm long, often in a slightly pubescent autumn the leaves are orange-red with yellow spots, the flowers are bright, purple-red, the fruit is rather elongated, formed in front of the leaves in April. The tree is of a low growth type and grows to a height of about 6 meters. The leaves are initially green, red-purple to black-purple, turning red in autumn. The flowers are small, purple, the fruit is red. Propagated by grafting or soft twigs. Prefers to grow in neutral alkaline soil, rich in organic matter, as well as well-drained, slightly acidic. Very favorable conditions were considered for its growth both in the sun and in partial shade. Treated as an ornamental plant, the color of its leaves is used for planting singly or in groups in landscape design, as it has an irreplaceable appearance on other trees. Introduced to the Botanical Garden. The seeds of this species were brought from Antwerp and sown in the Botanical Garden by academician A.A. Mavzhudov in 1971. In 1972, in the spring, the nursery was sown and the introduction of these species was studied, and in 1973 they were planted in the East Asian exposition. Currently, 1 adult year of the tree of this species grows in this exposition.